
This ambiguity is also why the calculator does not work with fractions, and can only divide when the result is an integer. Babylonian numerals (Languages), numerals Type the number of Babylonian numerals you want to convert in the text box, to see the results in the table.

It would be impossible to parse the input accurately without this system, as there could be several interpretations of the number entered. This is why the calculator above uses an additive system for input. Though large and small numbers could be represented, not having a symbol for zero left the number system with much ambiguity without context. Unlike our number system, the Babylonians represented numbers in base 60, so every number increases its value by a factor of 60 as you move left. The Babylonians used a positional number system, which allowed them to represent nearly any number, no matter how large or small.
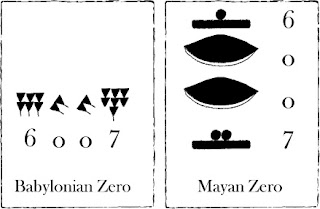
It was a vigesimal (base 20) number system. In this chapter, we wrap up with a specific example of a civilization that actually used a base system other than 10. Maya numerals was the number system of the Mayan civilization. The Babylonians used a base-sixty (sexigesimal) system. For example, the Natives of Queensland used a base-two system, counting as follows: “one, two, two and one, two two’s, much.” Some Modern South American Tribes have a base-five system counting in this way: “one, two, three, four, hand, hand and one, hand and two,” and so on. The Babylonians developed a number system with base 60 and the Maya with base 20. However, other civilizations have had a variety of bases other than ten. In part they used Base 60, the same number we see all around us in minutes, seconds, and degrees of a triangle or circle. Our own base-ten system probably arose from the fact that we have 10 fingers (including thumbs) on two hands. This third group is represented by the Maya, the Babylonian, and the Roman numerals. The Babylonians used this Base 10, but only in part. Use two different methods for converting numbers between basesĪs you might imagine, the development of a base system is an important step in making the counting process more efficient. To translate a Hindu-Arabic number into Mayan numerals, the number must be grouped into groups the size of each place value.Identify bases that have been used in number systems historically.Other types, mainly of historical interest, include Egyptian, Babylonian, Mayan, Greek, and Roman numerals. Arabic numerals (0-9) are the ones most commonly used today.

Become familiar with the history of positional number systems A numeral is a symbol used to represent a number.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
